Paiements SaaS
What is a Payment Aggregator?
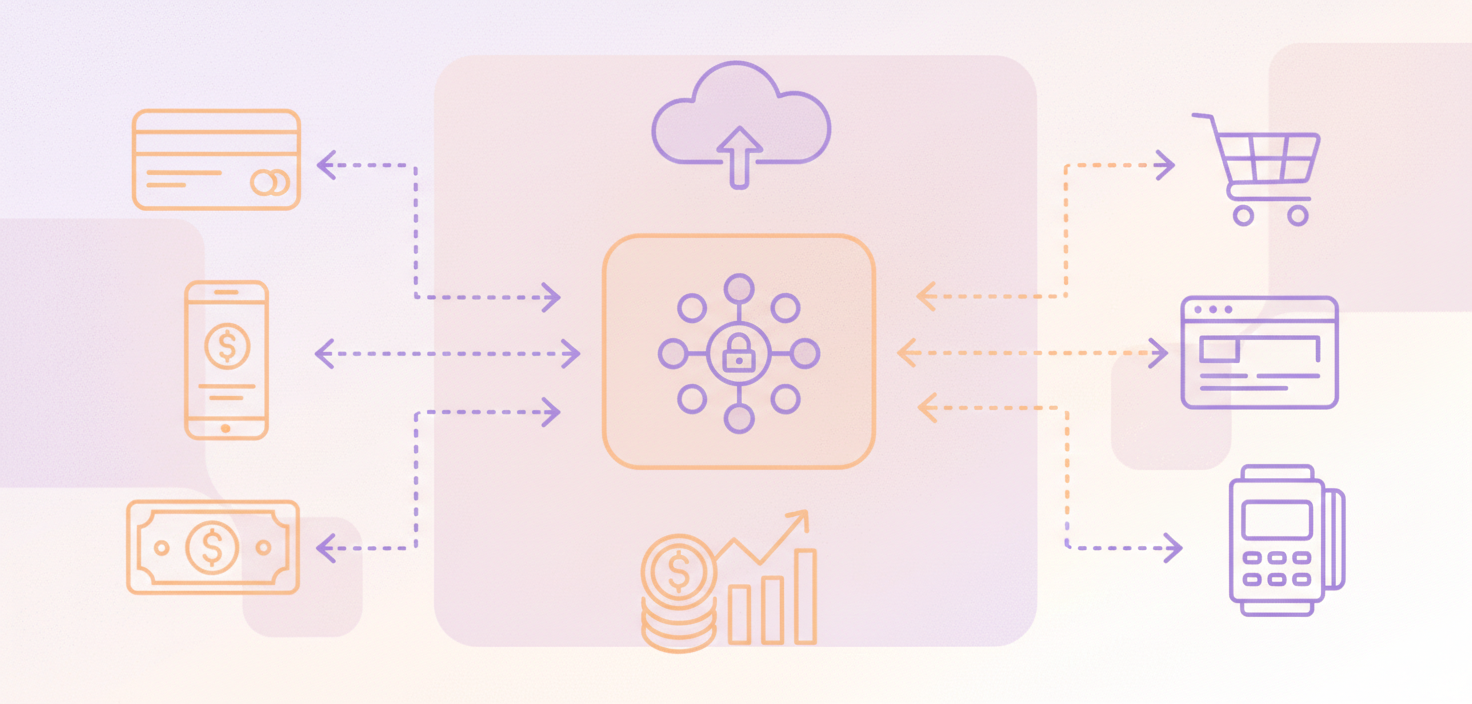
What is a payment aggregator?
A payment aggregator allows businesses to accept card and digital payments without opening their own merchant account. The payment aggregator has one master account that is used by each business to process transactions.
Partnering with a payment aggregator simplifies onboarding, especially for start-ups, SMBs, or newly launched businesses.
The payment aggregator manages connections to card networks, security systems, and banks so businesses can receive payments.
How does a payment aggregator process a payment?
A payment aggregator goes through the following steps when processing payments:
- A customer enters their payment details at checkout.
- The payment data is securely encrypted and tokenized.
- The aggregator runs fraud and risk verifcations.
- The transaction is sent through the card network to the customer’s issuing bank.
- The issuing bank approves or declines the payment.
- If approved, the payment is captured and later settled.
- The aggregator receives the funds and pays out to the merchant on its payout schedule.
It is important to notice that throughout the entire process, the SaaS business does not handle raw data at any point, reducing the compliance and security- related operations.
What are the main pros and cons of using a payment aggregator?
Payment aggregators offer both advantages and disadvantages.
|
Avantages |
Inconvénients |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
How is a payment aggregator different from a payment facilitator (PayFac)?
Both the payment aggregator andthe PayFac represent payment solutions that SaaS businesses can use. However, they are different in terms of features and approach.
|
Fonctionnalité |
Payment Aggregator |
Facilitateur de paiement (PayFac) |
|
Merchant Identity |
Processes all payments under a single merchant ID. |
Requires the use of a separate sub-merchant account for each company |
|
Provider Role |
The setup is simplified, as it needs to fit general requirements |
Takes care of compliance issues and manages bank connections for each account |
|
Flexibilité |
Limité |
dentification et validation de votre marché cible sont essentielles :ncreased flexibility in terms of pricing, risk and branding |
|
Infrastructure |
Requires minimal overhead. |
Requires more infrastructure and oversight from the provider. |
|
Merchant Fit |
Easiest to start with; ideal for smaller businesses. |
Better for larger or specialized platforms needing granular control. |
Which type is better for SaaS businesses?
Payment aggregators are a good fit for:
- Start-ups
- Low sales volume businesses
The reason for this is that payment aggregators facilitate faster launches.
PayFacs are an option for:
- Larger companies
- Rapidly expanding companies
This is because in these situations ,businesses require control over aspects like pricing and have greater customization needs.
How does this relate to a Merchant of Record model?
la solution Merchant of Record takes things to a different level, offering a higher level of service than the payment aggregator. The MOR model becomes the seller of the product, implying they do more than just payment processing.
The MOR also handles:
- end-to-end global taxation
- rejets de débit
- Conformité réglementaire
- payment support.
What should businesses look for when choosing a provider?
Here are the points to consider when selecting the payment aggregator to partner with:
- Strong security and PCI compliance
- Transparent fees and payout timing
- Reliable fraud and risk management
- Global payment method couverture
- Clear policies for holds and reserves
Ability to grow with the business (upgrade path to more control if needed)
Conclusion
Payment aggregators are a simple solution for accepting payments, and they work for ealy starts-ups and small companies. However, if SaaS companies are considering global expansion, considering the Merchant of Record model is an option.