Pricing Strategies
What is Cost-Plus Pricing in SaaS?
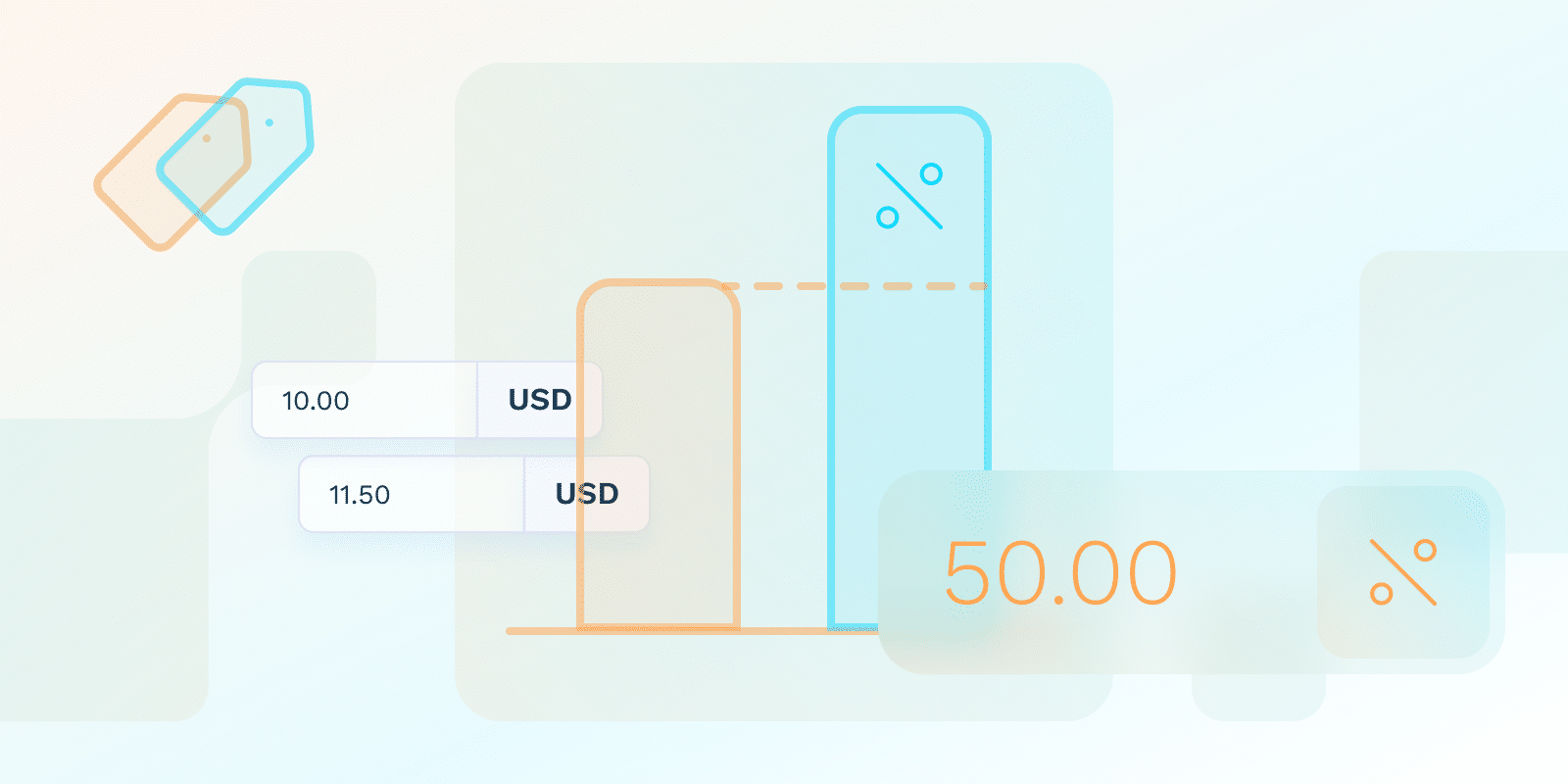
What is cost-plus pricing?
Cost-plus pricing for SaaS is a monetization strategy where on top of estimated production expenses, a percentage is added to establish the final price.
The added markup represents the desired profit margin.
When using this strategy, SaaS founders avoid underpricing their products, especially in the beginning.
Cost-plus strategy should be viewed as a starting point. Once you obtain some traction, you should perform a thorough market search and asses competitor pricing.
How is cost-plus pricing calculated?
Here are the steps to correctly calculate your product’s worth using the cost-plus pricing strategy:
- Step One: Start by identifying all production costs, direct and indirect, associated with your SaaS solution. These include product development, upkeep, and marketing expenses.
- Step Two: Determine your profit margin, also known as the markup, and set it as a percentage of the total production costs.
- Step Three: To calculate your product’s price tag, add the markup on top of the overall expenses.
For example, assuming your SaaS solution costs $10 to develop and you want to have a 15% profit margin on each sale, you would add a markup of $1.50 to your total expenses. Thus, your SaaS would have a price tag of $11.50.
Consider using cost-plus pricing to make a profit and just reach a balance point.
What are the benefits and drawbacks of using cost-plus pricing in SaaS?
Cost-plus pricing has advantages and disadvantages. Here are the major ones:
Pros
- Simple monetization practice: This pricing strategy provides a price tag calculation method.
- Assured earnings: By determining your product’s total ownership costs and adding a profit margin, each transaction can generate revenue.
Cons:
- Overlook willingness to pay: Cost-plus monetization doesn’t consider competition pricing.
- Underrate product value: This strategy puts development expenses first.
What industries and SaaS businesses are most suited to using cost-plus pricing?
This approach can be used in:
- Highly-customized software development: SaaS products that provide targeted solutions to specific requirements can employ the cost-plus strategy.
- Infrastructure services: This monetization strategy is suitable in the case of organizations like Amazon Web Services or Microsoft Azure due to higher development and maintenance expenses, as well as possible customization requirements.
- Startups and Early-stage SaaS Businesses: For businesses found in the initial growth stage, cost-plus pricing is an alternative as it offers additional expansion resources.
| Business Type | Characteristics | Cost-Plus Pricing Fit |
|---|---|---|
| Business Model Segments | ||
| Highly-Customized Software | Targeted solutions for specific requirements | High Fit – Helps recover complex development costs |
| Infrastructure Services | High development and maintenance expenses | Very High Fit – Ensures cost recovery for complex infrastructure |
| Startups and Early-Stage SaaS | Limited resources, need for financial predictability | Good Fit – Provides a straightforward pricing baseline |
| Pricing Complexity | ||
| Simple Product Offerings | Straightforward functionality, consistent costs | Excellent Fit – Easy to calculate, transparent pricing |
| Complex, Multi-Feature Products | Varied development and maintenance expenses | Moderate Fit – Requires careful cost allocation |
| Market Dynamics | ||
| Emerging Markets | Less competitive, developing pricing standards | High Fit – Provides a rational pricing approach |
| Saturated Markets | High competition, price-sensitive customers | Low Fit – Requires supplementing with market research |
While cost-plus monetization is the primary approach, it is relevant to assess the competitor pricing when determining your markup.
How can SaaS founders use cost-plus pricing to optimize their pricing strategies?
Cost-plus pricing can be used as a baseline.
Having production expenses laid out, you can move on to market research and competitor pricing evaluation. Doing so, you will be able to understand your customers’ willingness to pay.
Additionally, use value-based pricing to adjust your monetization approach and increase the markup, considering the value your offering brings users. This will help you differentiate your software from others on the market.
Conclusion
Cost-plus pricing is an approach to business profitability. However, while it can be an appropriate alternative in the early growth stages, SaaS founders should consider combining it with other strategies to ensure pricing flexibility.